Arthritis simply means widespread damage to the joint cartilage. The most common form of arthritis known as osteoarthritis is a degenerative or “wear and tear” kind of arthritis where the cartilage gradually wears out over time. There is another type of arthritis known as inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), gout or pseudogout. These type of arthritis are part of the systemic illness and in some cases, such as RA, the body produces abnormal antibodies that attack its own joints (auto-antibodies).
The three most common types of inflammatory arthritis that affect the joints are:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis – a systemic disease of the immune system that usually affects multiple joints on both sides of the body at the same time
- Ankylosing Spondylitis – a chronic inflammation of the spine and the sacroiliac joint (the point where the spine meets the pelvic bone) that can also cause inflammation in other joints
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – an autoimmune disease in which the body harms its own healthy cells and tissues
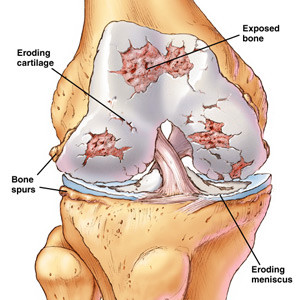
Signs and Symptoms of Arthritis
The classic sign of arthritis is joint pain. Pain is often associated with stiffness and these symptoms can be worse in the morning. Occasionally, there is warmth and redness over the affected joint. In advanced stages of arthritis, joint deformities set in, especially in knee arthritis.
Treatment of Arthritis
-
Nonsurgical Treatment
We usually co-manage such cases with the rheumatologist.
- Anti-inflammatory medications, such as aspirin or ibuprofen, may help reduce the inflammation.
- Corticosteroids are potent anti-inflammatories, part of a drug category known as symptom-modifying antirheumatic drugs (SMARDs). They can be taken orally, by injection into the joints, or as creams applied to the skin. The potential side effects of this medication include osteonecrosis or avascular necrosis (bone death).
- Methotrexate and sulfasalazine may be prescribed to help retard the progression of the disease. These medications are part of a drug category called disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). For example, tumour necrosis factor is one of the substances that seem to cause inflammation in people with arthritis. Newer drugs that work against this factor seem to have a positive effect on arthritis in some patients as well.
- Physical therapy may help you increase the range of motion, and strengthening exercises may help maintain muscle tone. Swimming is a preferred exercise for people with ankylosing spondylitis.
- Assistive devices, such as a cane or walker may make it easier for you to do daily living activities.
-
Surgical Treatment
Surgery might be required if the above treatment methods fail. Surgery might be required to treat arthritis itself or the complications from the medications used to treat arthritis (eg. osteonecrosis). The most common surgical procedures performed are :
- Total hip replacement or total knee replacement to provide pain relief, deformity correction and improvement of the quality of life.
- Core decompression and bone grafting for the treatment of osteonecrosis (bone death) from side effects of corticosteroid consumption for the treatment of inflammatory arthritis.
Looking For A Reliable Knee Orthopaedic Specialist?
Fast Medical Attention, Transparent Fees
Make an appointment for comprehensive care for your knee problems!
