Osteotomy literally means “cutting of the bone.” In a knee osteotomy, either the tibia (shinbone) or femur (thighbone) is cut and then realigned to relieve pressure on the affected part of the knee. It is also used to correct or straighten out lower limbs that are wrongly aligned.
Knee osteotomy is performed when you have osteoarthritis that has damaged just one side of the knee joint. By shifting your weight off the damaged side of the joint onto the normal side, an osteotomy can relieve pain and significantly improve function in your arthritic knee.
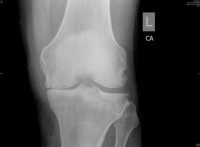
Description
Osteoarthritis can develop when the bones of your knee and leg do not line up properly. This can put extra stress on on either the inner (medial) or outer (lateral) side of your knee. Over time, this extra pressure can wear away the smooth cartilage that protects the bones, causing pain and stiffness in your knee.

Advantages and Disadvantages
Knee osteotomy has three goals:
- To transfer weight from the arthritic part of the knee to a healthier area
- To correct poor knee alignment
- To prolong the life span of the knee joint
By preserving your own knee anatomy, a successful osteotomy may delay the need for a joint replacement for several years. Another advantage is that there are no restrictions on physical activities after an osteotomy – you will be able to comfortably participate in your favorite activities, even high impact exercise.
Osteotomy does have disadvantages. For example, pain relief is not as predictable after osteotomy compared with a partial or total knee replacement . Because you cannot put your body weight on your leg after osteotomy (from 6-12 weeks while the cut bone is healing), it takes longer to recover from an osteotomy procedure than a partial knee replacement.
In some cases, having had an osteotomy can make later knee replacement surgery more challenging.
The recovery is typically longer than a partial knee replacement because of pain and the need to be non-weightbearing for 6-12 weeks post surgery.
Because results from total knee replacement and partial knee replacement have been so successful, the number of knee osteotomy procedures performed has decreased significantly. Nevertheless, it remains an option for a specific group of patients – young patients with single compartment osteoarthritis of the knee and who wish to continue with high-impact activities after surgery
Procedure
Most osteotomies for knee arthritis are done on the tibia (shinbone) to correct a bowlegged (varus) alignment that is putting too much stress on the inside (medial aspect) of the knee. An osteotomy aims to straighten out the lower limb so that weight is redistributed from the overloaded painful side to the other side of the knee. This releases pressure from the painful side and provides pain relief.
Tibial osteotomy was first performed in Europe in the late 1950s and brought to the United States in the 1960s. This procedure is sometimes called a high tibial osteotomy (HTO).
There are 2 techniques used and they are called the opening wedge or closing wedge HTO. Dr Lee’s preference is the opening wedge HTO.
Candidates for Knee Osteotomy
Knee osteotomy is most effective for young, active patients who are 40 to about 60 years old. Good candidates have pain on only one side of the knee, and no pain under the kneecap. Knee pain should be brought on mostly by activity, as well as standing for a long period of time.
Candidates should be able to fully straighten the knee and bend it at least 90 degrees.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis are not good candidates for osteotomy. Your orthopaedic surgeon will help you determine whether a knee osteotomy is suited for you.
Surgical Procedure
A knee osteotomy operation typically lasts between 1 and 2 hours.
Dr Lee will make an incision at the front of your knee, starting below your kneecap. He would have planned out the correct amount of correction of the alignment before the surgery. With an oscillating saw, he will make a single cut along the inside (medial) aspect of the tibia and this cut is slowly jacked open to a certain angle that he had calculated.
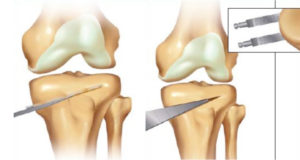
This space is then filled with bone graft and the space held apart with plates and screws.
After surgery care is important for your osteotomy recovery, it is important you follow the steps recommended by your surgeon.
Looking For A Reliable Knee Orthopaedic Specialist?
Fast Medical Attention, Transparent Fees
Make an appointment for comprehensive care for your knee problems!